Did you know that websites using schema markup have a 30% higher click-through rate? Schema markup is a powerful SEO tool that helps search engines understand your content better. It enhances the visibility of your website by showing rich snippets in search results.
Different types of Schema markup
Schema markup comes in various types based on the content it describes. Some popular types include:
- Organization Schema
- Local Business Schema
- Product Schema
- Review Schema
- Article Schema
- FAQ Schema
- Event Schema
Different Schema markup format
There are three common formats used for schema markup:
JSON-LD
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is the most recommended schema format by Google. It is easy to implement as a block of code in the HTML header or body, keeping it separate from the actual content.
Microdata
Microdata is embedded directly within the HTML tags of your page. While it serves the same purpose as JSON-LD, it can make your HTML code more cluttered and harder to maintain.
RDFa
RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) embeds schema markup within HTML as attributes. It is useful when linking data from multiple sources but is less popular than JSON-LD or Microdata.
Implementing Schema markup manually
To manually add schema markup to your webpage, follow these steps:
Choose the Right Schema Type: Decide on the type of schema that best suits your content. For example, use Article Schema for blog posts, Product Schema for product pages, or FAQ Schema for frequently asked questions.
Generate Schema Markup Code: Use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper. Select the schema type you want to use and enter the URL of your webpage or the raw HTML. Highlight the elements on the page, like headings or product details, and tag them with appropriate schema properties.
Copy the Generated Code: After tagging your content, the tool will generate the required schema markup in JSON-LD format. Copy the code.
Insert the Schema Markup into Your HTML: Open the HTML file of the webpage where you want to implement the schema. Paste the JSON-LD code into the or section of your HTML, ensuring it does not interfere with the existing content.
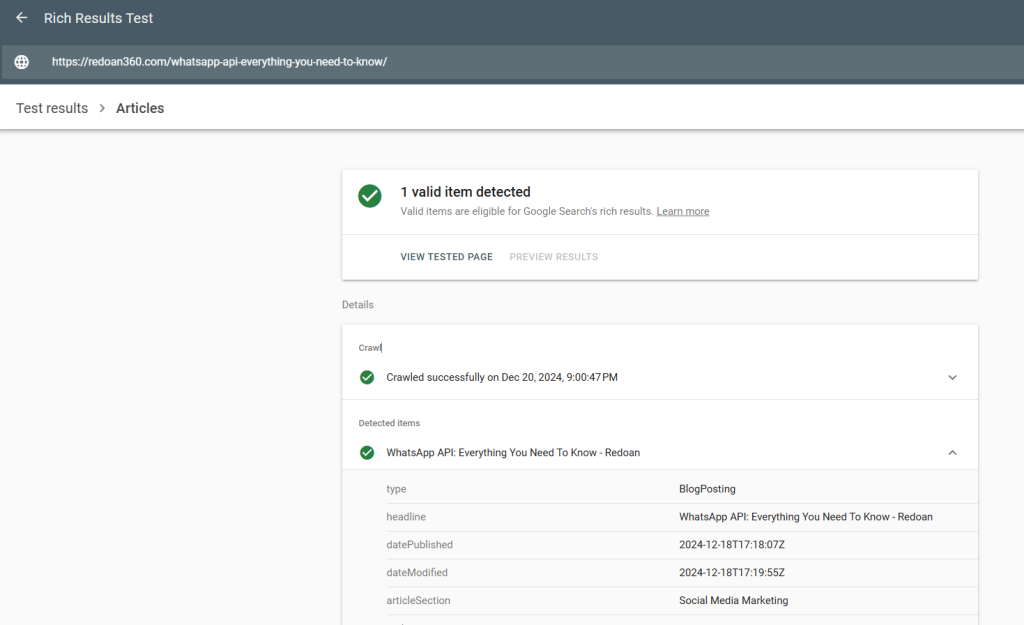
Test the Markup: Use Google’s Rich Results Test or the Schema Markup Validator to test your schema. Make sure there are no errors, and it is eligible for rich results.
Publish the Webpage: Once everything is tested and validated, publish or update the webpage to make the schema markup live.
Implementing schema markup with a plugin
If you’re using a CMS like WordPress, plugins make adding schema markup easy. Here’s how to do it:
Choose a Schema Markup Plugin: Select a reliable schema markup plugin like Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or Schema Pro. These plugins allow you to add structured data without coding knowledge.
Install the Plugin:
- Go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to Plugins > Add New.
- Search for your preferred schema plugin (e.g., Schema Pro).
- Click Install Now, and then activate the plugin.
Configure the Plugin Settings: After activation, go to the plugin’s settings. Some plugins like Yoast SEO automatically add basic schema to your entire site, but you can fine-tune the settings for specific pages or posts:
- In Yoast SEO, go to Search Appearance > Schema and customize the schema types for your homepage, posts, or pages.
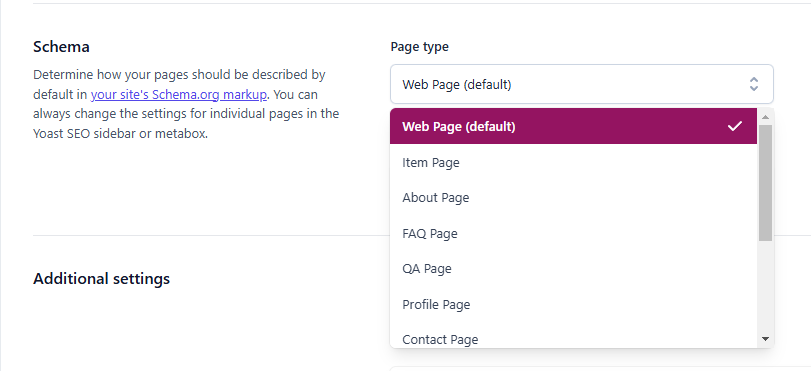
- In Schema Pro, navigate to Schema Types and choose the type of schema you want to add (e.g., product, article, FAQ, etc.).
- You can also configure Schema with rankmath plugin in a similar way.
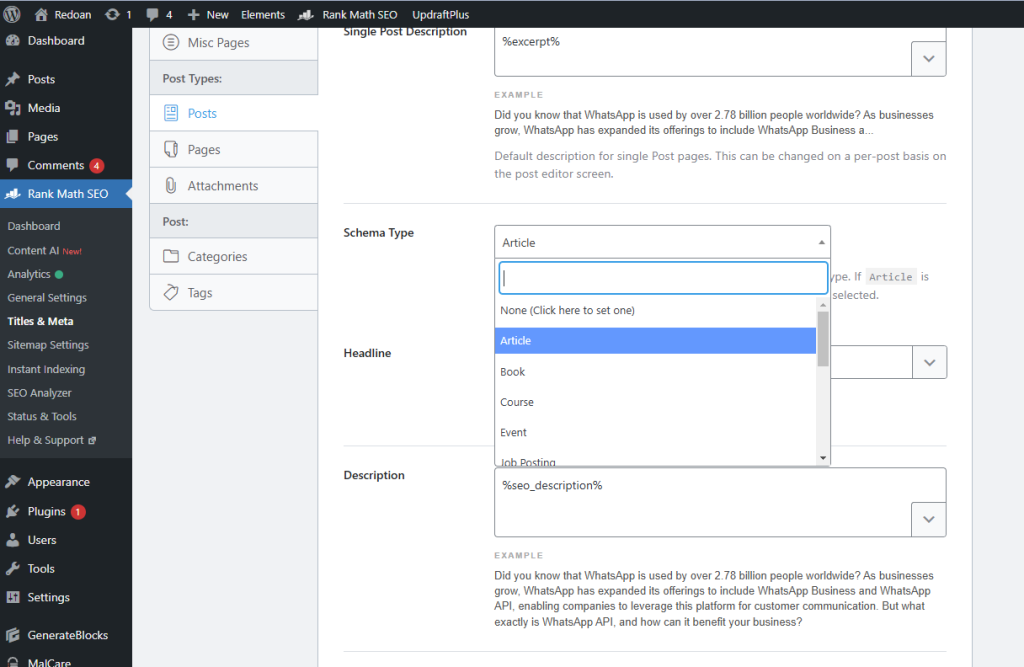
Add Schema to Pages or Posts
- Go to the post or page you want to edit.
- Scroll down to the schema section (Yoast SEO or Rank Math adds this automatically).
- Select the appropriate schema type, such as FAQ Schema, Product Schema, or Article Schema.
- Fill in the necessary fields like product details, article information, or FAQs.
Save and Update the Page: Once the schema markup has been added, click Save or Update to publish the changes to the live site.
Schema markup best practices
Use JSON-LD Format
Google recommends using JSON-LD for schema markup as it’s cleaner, easier to implement, and keeps the code separate from your HTML.
Select the Most Specific Schema Type
Always choose the most appropriate and specific schema type relevant to your content. For example, use Product Schema for products and FAQ Schema for frequently asked questions.
Add Schema to Important Pages
Prioritize applying schema markup to pages that matter most, such as product pages, service pages, and articles. These pages are likely to benefit more from rich snippets in search results.
Test Your Schema Regularly
After implementing schema markup, always use Google’s Rich Results Test or the Schema Markup Validator to ensure your markup is error-free and properly implemented.
Avoid Overloading with Multiple Schemas
While multiple schemas are allowed, avoid adding irrelevant schema types to a single page. Focus on the schema types that enhance user experience and are relevant to the page’s content.
Keep Your Schema Code Updated
Ensure that your schema markup is regularly updated to reflect any changes to your content. Outdated schema may confuse search engines and result in errors or missing rich snippets.
Include Essential Properties
Always include all the recommended and essential properties for each schema type. Missing key properties can prevent search engines from fully understanding your content.
Use Breadcrumbs Schema
Implement breadcrumb schema to improve site navigation for users and help search engines understand your site structure. Breadcrumbs also enhance the visibility of your URLs in search results.
Don’t Spam Keywords in Schema
Avoid keyword stuffing in your schema markup. Stick to providing accurate, clear information that genuinely reflects the content of the page.
Monitor Your Markup in Google Search Console
Use the Enhancements section in Google Search Console to monitor your schema markup’s performance. It alerts you to any errors and provides suggestions for improvements.
FAQ
Is multiple schemas allowed for a single webpage?
Yes, multiple schemas can be used on a single webpage. For example, a product page can have both Product and Review schema markup. Just ensure they are relevant to the content on the page.
Is multiple schemas allowed for a single webpage?
Yes, multiple schemas can be used on a single webpage. For example, a product page can have both Product and Review schema markup. Just ensure that the schemas are relevant to the content on the page and correctly implemented.
Does schema markup affect SEO rankings?
Schema markup itself does not directly affect SEO rankings, but it enhances the way your content is displayed in search results. By improving click-through rates with rich snippets, it can indirectly boost your SEO performance.
How long does it take for schema markup to show in search results?
Once schema markup is implemented and validated, it can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks for rich snippets to appear in search results, depending on how often search engines crawl your website.
Can schema markup break my website?
Incorrect implementation of schema markup, especially when embedding it within the HTML, can cause errors on your website. Always test your schema using Google’s tools to avoid issues.
Is schema markup necessary for all websites?
While schema markup is not required, it is highly beneficial for websites aiming to improve their visibility in search engines. E-commerce, local businesses, and content-heavy websites can especially benefit from rich snippets enabled by schema markup.
